What Animals Eat and Lives According to Their Structure
Learning Objectives
- Distinguish essential, beneficial, macro- and micro-food requirements for plants and animals
- Predict the symptoms of nutrient deficiencies in plants and animals
- Draw the diverseness of adaptations for acquisition of nutrients in plants and animals
Living Cells Need Materials to Grow: Nutrients
The information beneath was adapted from OpenStax Biology 22.iii, OpenStax Biology 23.2, and OpenStax Biology 24.1
Macronutrients
Cells are essentially a well-organized assemblage of macromolecules and water. Recall that macromolecules are produced by the polymerization of smaller units chosen monomers. For cells to build all of the molecules required to sustain life, they need certain substances, collectively called nutrients. When prokaryotes grow, they obtain their nutrients from the surroundings. Nutrients that are required in large amounts are called macronutrients, whereas those required in smaller or trace amounts are called micronutrients. Just a scattering of elements are considered macronutrientsâ€"carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur. (A mnemonic for remembering these elements is the acronym CHONPS.)
Why are these macronutrients needed in large amounts? They are the components of organic compounds in cells, including water. Carbon is the major element in all macromolecules: carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, and many other compounds. Carbon accounts for near 50 percent of the limerick of the jail cell. Nitrogen represents 12 percent of the total dry out weight of a typical cell and is a component of proteins, nucleic acids, and other jail cell constituents. Virtually of the nitrogen available in nature is either atmospheric nitrogen (North2) or another inorganic form. Diatomic (N2) nitrogen, still, can exist converted into an organic class only by sure organisms, called nitrogen-fixing organisms. Both hydrogen and oxygen are function of many organic compounds and of water. Phosphorus is required by all organisms for the synthesis of nucleotides and phospholipids. Sulfur is part of the structure of some amino acids such as cysteine and methionine, and is too present in several vitamins and coenzymes. Other important macronutrients are potassium (K), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), and sodium (Na). Although these elements are required in smaller amounts, they are very important for the structure and function of the prokaryotic prison cell.
Micronutrients
In add-on to these macronutrients, prokaryotes require various metallic elements in small amounts. These are referred to equally micronutrients or trace elements. For example, fe is necessary for the function of the cytochromes involved in electron-transport reactions. Some prokaryotes crave other elementsâ€"such as boron (B), chromium (Cr), and manganese (Mn)â€"primarily as enzyme cofactors.
Nutritional Needs and Adaptations in Plants
The information below was adjusted from OpenStax Biological science 31.1, OpenStax Biology 31.2, and OpenStax Biological science 31.3
Essential Nutrients
Plants require only calorie-free, water and about xx elements to support all their biochemical needs: these 20 elements are called essential nutrients. For an element to be regarded as essential, three criteria are required: ane) a constitute cannot complete its life cycle without the element; two) no other chemical element can perform the function of the element; and iii) the element is directly involved in plant diet.
| Essential Elements for Establish Growth | |
|---|---|
| Macronutrients | Micronutrients |
| Carbon (C) | Iron (Fe) |
| Hydrogen (H) | Manganese (Mn) |
| Oxygen (O) | Boron (B) |
| Nitrogen (N) | Molybdenum (Mo) |
| Phosphorus (P) | Copper (Cu) |
| Potassium (K) | Zinc (Zn) |
| Calcium (Ca) | Chlorine (Cl) |
| Magnesium (Mg) | Nickel (Ni) |
| Sulfur (S) | Cobalt (Co) |
| Sodium (Na) | |
| Silicon (Si) | |
Macronutrients and Micronutrients
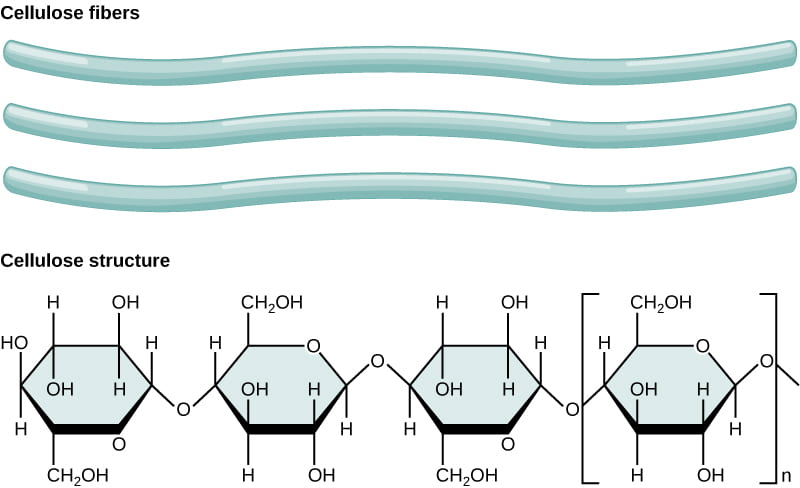
The essential elements can be divided into two groups: macronutrients and micronutrients. Nutrients that plants require in larger amounts are called macronutrients. About one-half of the essential elements are considered macronutrients: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium and sulfur. The first of these macronutrients, carbon (C), is required to class carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, and many other compounds; it is therefore nowadays in all macromolecules. On average, the dry weight (excluding water) of a cell is 50 pct carbon. Every bit shown below, carbon is a key part of plant biomolecules.
Three cellulose fibers and the chemical structure of cellulose is shown. Cellulose consists of unbranched chains of glucose subunits that course long, straight fibers.
Cellulose, the main structural component of the plant cell wall, makes upward over thirty percent of plant matter. It is the most abundant organic compound on earth. Plants are able to make their own cellulose, but demand carbon from the air to practise so.
The next most abundant element in plant cells is nitrogen (Due north); it is part of proteins and nucleic acids. Nitrogen is also used in the synthesis of some vitamins. While there is an overwhelming corporeality of nitrogen in the air (79% of the atmosphere is nitrogen gas), the nitrogen in the air is non biologically available due to the triple bond betwixt the nitrogen atoms. Only a few species of bacteria are capable of "fixing" nitrogen to make it bioavailable; thus nitrogen is often a limiting gene for constitute growth.
Phosphorus (P), some other macromolecule, is necessary to synthesize nucleic acids and phospholipids. Every bit part of ATP, phosphorus enables nutrient energy to be converted into chemical free energy through oxidative phosphorylation. Likewise, light energy is converted into chemic energy during photophosphorylation in photosynthesis, and into chemical energy to be extracted during respiration. Phosphorous is typically available in a form that is not readily taken up by institute roots; the form that is bioavailable is present in small quantities and rapidly "fixed" into the bioavailable form once again. Phosphorus is therefore often a limiting cistron for found growth.
Potassium (K) is important because of its office in regulating stomatal opening and endmost. Every bit the openings for gas commutation, stomata help maintain a salubrious water balance; a potassium ion pump supports this procedure. Potassium may be nowadays at low concentrations in some types of soil, and it is the third almost common limiting cistron for plant growth.
Other essential macronutrients: Hydrogen and oxygen are macronutrients that are part of many organic compounds, and as well form water. Oxygen is necessary for cellular respiration; plants use oxygen to store energy in the form of ATP. Sulfur is part of certain amino acids, such as cysteine and methionine, and is nowadays in several coenzymes. Sulfur also plays a role in photosynthesis as function of the electron ship chain, where hydrogen gradients play a primal function in the conversion of light energy into ATP.
Magnesium (Mg) and calcium (Ca) are too of import macronutrients. The role of calcium is twofold: to regulate food transport, and to support many enzyme functions. Magnesium is important to the photosynthetic process. These minerals, forth with the micronutrients, which are described below, besides contribute to the plant’s ionic balance.
In addition to macronutrients, organisms require various elements in small-scale amounts. These micronutrients, or trace elements, are present in very pocket-size quantities. They include boron (B), chlorine (Cl), manganese (Mn), atomic number 26 (Fe), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), nickel (Ni), silicon (Si), and sodium (Na).
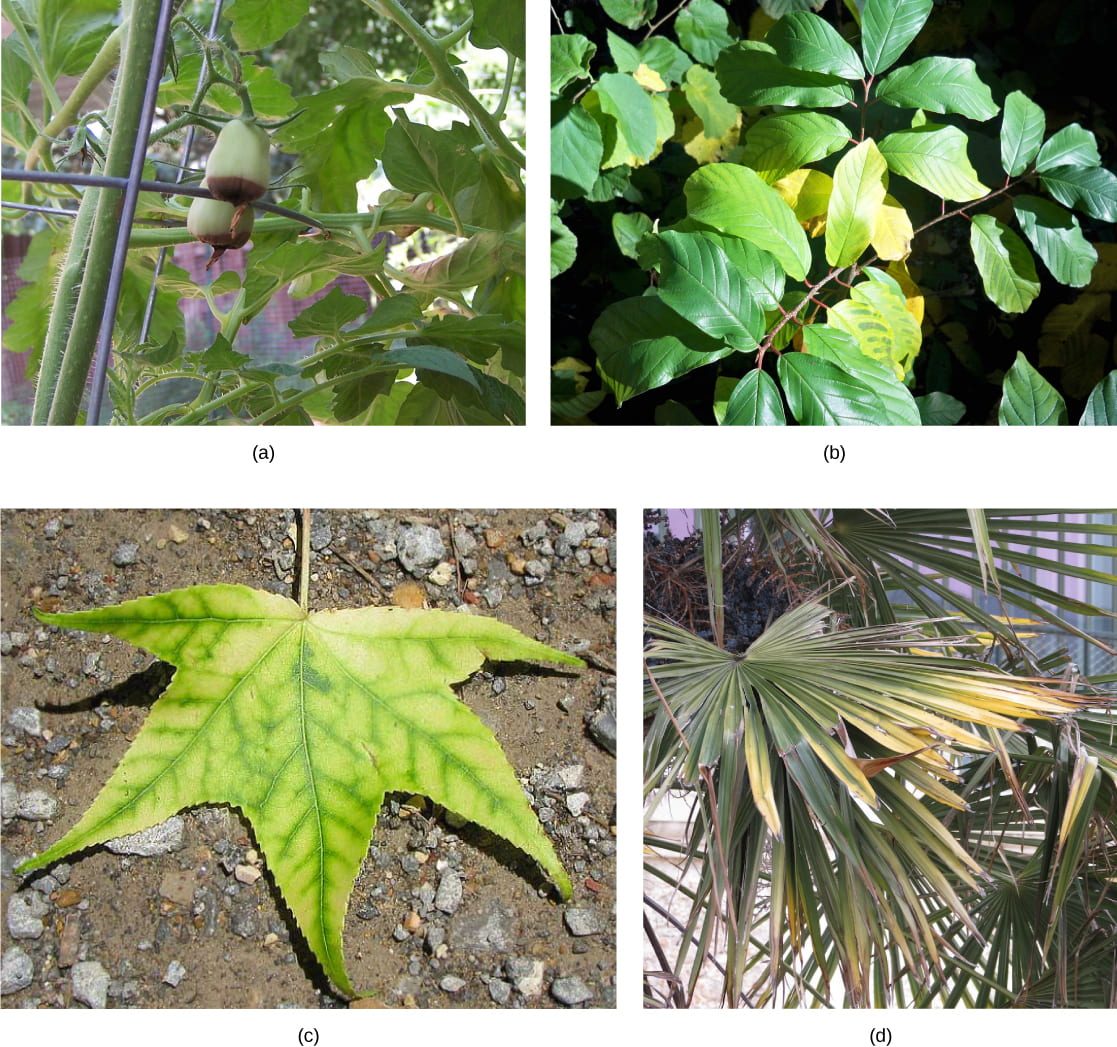
Deficiencies in any of these nutrients, especially the macronutrients, tin can adversely affect plant growth. Depending on the specific nutrient, a lack tin cause stunted growth, dull growth, or chlorosis (yellowing of the leaves). Farthermost deficiencies may result in leaves showing signs of cell expiry.
Photo (a) shows a tomato found with ii green tomato fruits. The fruits accept turned dark brown on the bottom. Photo (b) shows a plant with green leaves; some of the leaves take turned yellow. Photo (c) shows a five-lobed leaf that is xanthous with green veins. Photo (d) shows green palm leaves with xanthous tips. Nutrient deficiency is evident in the symptoms these plants show. This (a) grape lycopersicon esculentum suffers from blossom stop rot acquired by calcium deficiency. The yellowing in this (b) Frangula alnus results from magnesium deficiency. Inadequate magnesium too leads to (c) intervenal chlorosis, seen here in a sweetgum leaf. This (d) palm is affected by potassium deficiency. (credit c: modification of piece of work by Jim Conrad; credit d: modification of piece of work by Malcolm Manners)
Plants obtain inorganic elements from the soil, which serves as a natural medium for land plants. Soil is the outer loose layer that covers the surface of Earth. Soil quality is a major determinant, along with climate, of plant distribution and growth. Soil quality depends not but on the chemical limerick of the soil, only also the topography (regional surface features) and the presence of living organisms. In agriculture, the history of the soil, such as the cultivating practices and previous crops, alter the characteristics and fertility of that soil.
Plants obtain nutrient in two dissimilar ways. Autotrophic plants can brand their own food from inorganic raw materials, such as carbon dioxide and h2o, through photosynthesis in the presence of sunlight. Green plants are included in this group. Some plants, however, are heterotrophic: they are totally parasitic and lacking in chlorophyll. These plants, referred to every bit holo-parasitic plants, are unable to synthesize organic carbon and draw all of their nutrients from the host plant.
Plants may too do good from microbial partners in nutrient acquisition. Detail species of bacteria and fungi have co-evolved forth with sure plants to create a mutualistic symbiotic relationship with roots. This improves the diet of both the plant and the microbe. The germination of nodules in legume plants and mycorrhization can be considered amid the nutritional adaptations of plants. Still, these are not the only type of adaptations that we may discover; many plants take other adaptations that let them to thrive under specific conditions.
Nutrients from Other Sources
Some plants cannot produce their ain food and must obtain their nutrition from outside sources. This may occur with plants that are parasitic or saprophytic. Some plants are mutualistic symbionts, epiphytes, or insectivorous.
Parasitic Plants
A parasitic plant depends on its host for survival. Some parasitic plants have no leaves. An example of this is the clump, which has a weak, cylindrical stalk that coils effectually the host and forms suckers. From these suckers, cells invade the host stalk and grow to connect with the vascular bundles of the host. The parasitic plant obtains h2o and nutrients through these connections. The found is a full parasite (a holoparasite) because it is completely dependent on its host. Other parasitic plants (hemiparasites) are fully photosynthetic and but use the host for h2o and minerals. At that place are about 4,100 species of parasitic plants.
Saprophytes
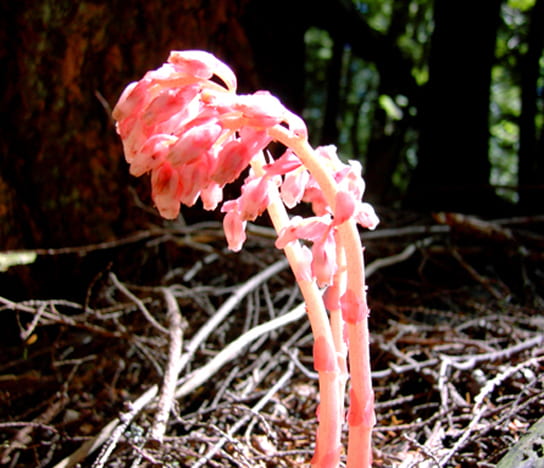
A saprophyte is a plant that does non have chlorophyll and gets its nutrient from dead affair, similar to leaner and fungi (note that fungi are often chosen saprophytes, which is incorrect, considering fungi are not plants). Plants like these use enzymes to convert organic food materials into simpler forms from which they can absorb nutrients. Most saprophytes do non directly digest dead matter: instead, they parasitize fungi that digest expressionless matter, or are mycorrhizal, ultimately obtaining photosynthate from a fungus that derived photosynthate from its host. Saprophytic plants are uncommon; merely a few species are described.
Photo shows a institute with light pink stems reminiscent of asparagus. Bud-similar appendages grow from the tips of the stems. Saprophytes, similar this Dutchmen’s pipe (Monotropa hypopitys), obtain their nutrient from expressionless matter and do non have chlorophyll. (credit: modification of piece of work by Iwona Erskine-Kellie)
Symbionts
A symbiont is a found in a symbiotic relationship, with special adaptations such as mycorrhizae or nodule formation. Fungi too form symbiotic associations with cyanobacteria and greenish algae (called lichens). Lichens can sometimes be seen equally colorful growths on the surface of rocks and trees. The algal partner (phycobiont) makes food autotrophically, some of which it shares with the mucus; the fungal partner (mycobiont) absorbs water and minerals from the surround, which are made bachelor to the greenish alga. If one partner was separated from the other, they would both die.
Epiphytes
An epiphyte is a plant that grows on other plants, but is non dependent upon the other plant for diet. Epiphytes have two types of roots: clinging aerial roots, which absorb nutrients from humus that accumulates in the crevices of trees; and aerial roots, which blot wet from the atmosphere.
Insectivorous Plants
An insectivorous plant has specialized leaves to attract and digest insects. The Venus flytrap is popularly known for its insectivorous mode of nutrition, and has leaves that work equally traps. The minerals it obtains from casualty compensate for those lacking in the boggy (low pH) soil of its native North Carolina littoral plains. There are three sensitive hairs in the heart of each half of each leafage. The edges of each leaf are covered with long spines. Nectar secreted by the plant attracts flies to the foliage. When a fly touches the sensory hairs, the leaf immediately closes. Adjacent, fluids and enzymes break downward the prey and minerals are absorbed by the leafage. Since this plant is pop in the horticultural trade, it is threatened in its original habitat.
A Venus flytrap has specialized leaves to trap insects. (credit: "Selena North. B. H."/Flickr)
Nutritional Needs and Adaptations in Animals
The data below was adapted from OpenStax Biology 34.0, OpenStax Biological science 34.1 OpenStax Biology 34.ii
Most animals obtain their nutrients past the consumption of other organisms. At the cellular level, the biological molecules necessary for animal function are amino acids, lipid molecules, nucleotides, and simple sugars. Even so, the food consumed consists of protein, fat, and circuitous carbohydrates. Animals must convert these macromolecules into the simple molecules required for maintaining cellular functions, such as assembling new molecules, cells, and tissues. The conversion of the food consumed to the nutrients required is a multi-pace process involving digestion and assimilation. During digestion, nutrient particles are broken down to smaller components, and subsequently, they are captivated past the body.
Animals obtain their nutrition from the consumption of other organisms. Depending on their diet, animals can be classified into the post-obit categories: plant eaters (herbivores), meat eaters (carnivores), and those that eat both plants and animals (omnivores). The nutrients and macromolecules present in food are non immediately attainable to the cells. There are a number of processes that alter food inside the animal trunk in order to brand the nutrients and organic molecules accessible for cellular function. Equally animals evolved in complexity of class and part, their digestive systems have also evolved to adjust their various dietary needs.
Herbivores, Omnivores, and Carnivores
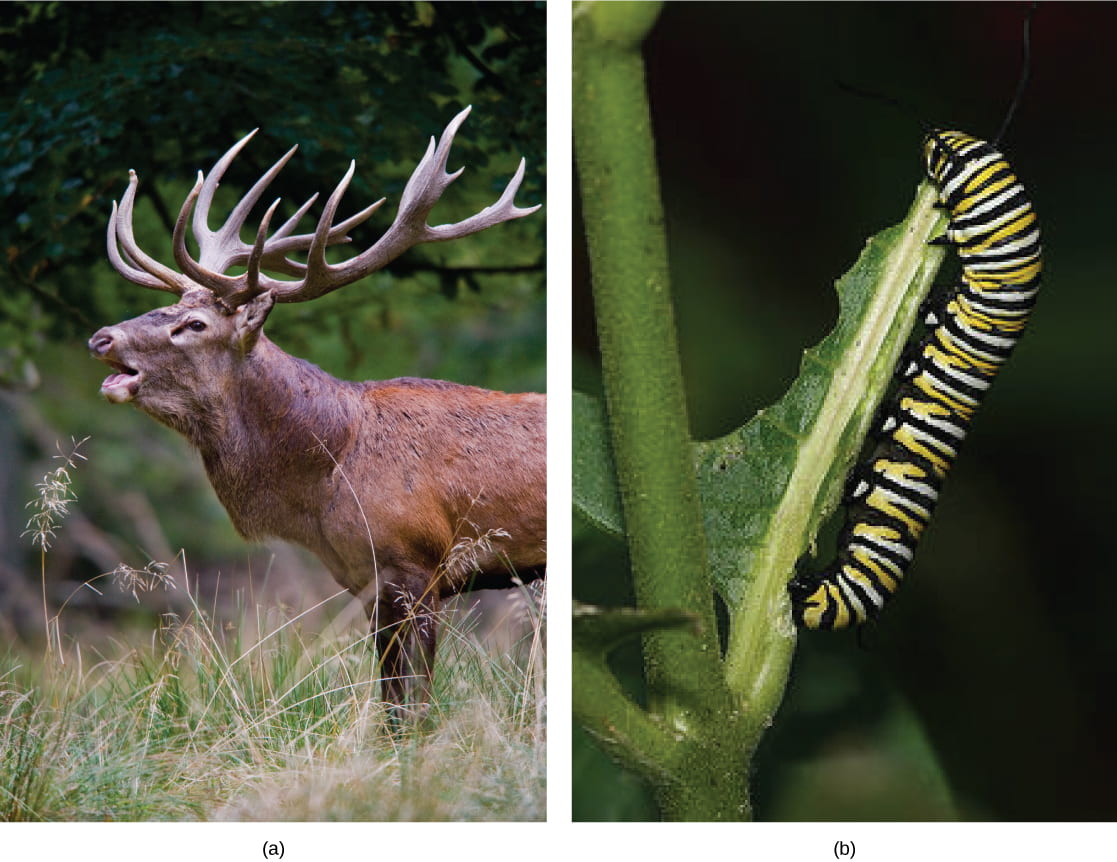
Herbivores are animals whose principal nutrient source is establish-based. Examples of herbivores, as shown below, include vertebrates similar deer, koalas, and some bird species, every bit well equally invertebrates such as crickets and caterpillars. These animals accept evolved digestive systems capable of handling large amounts of found material. Herbivores can be further classified into frugivores (fruit-eaters), granivores (seed eaters), nectivores (nectar feeders), and folivores (leaf eaters).
Herbivores, like this (a) mule deer and (b) monarch caterpillar, eat primarily plant material. (credit a: modification of work by Beak Ebbesen; credit b: modification of work by Doug Bowman)
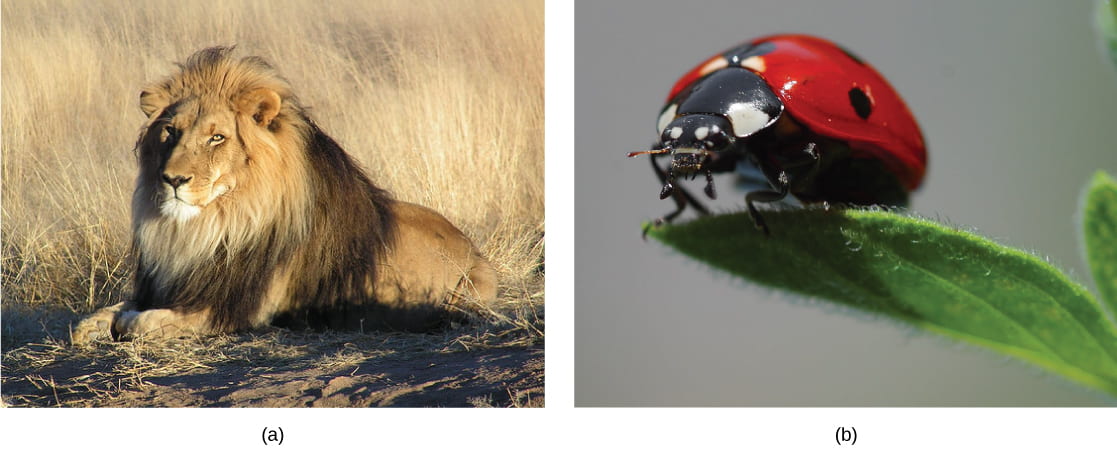
Carnivores are animals that eat other animals. The word carnivore is derived from Latin and literally ways "meat eater." Wild cats such as lions and tigers are examples of vertebrate carnivores, as are snakes and sharks, while invertebrate carnivores include bounding main stars, spiders, and ladybugs. Obligate carnivores are those that rely entirely on animal flesh to obtain their nutrients; examples of obligate carnivores are members of the cat family, such equally lions and cheetahs. Facultative carnivores are those that likewise consume not-brute food in addition to animate being food. Note that there is no clear line that differentiates facultative carnivores from omnivores; dogs would exist considered facultative carnivores.
Carnivores similar the (a) lion eat primarily meat. The (b) ladybug is also a carnivore that consumes small insects called aphids. (credit a: modification of work past Kevin Pluck; credit b: modification of work past Jon Sullivan)
Â
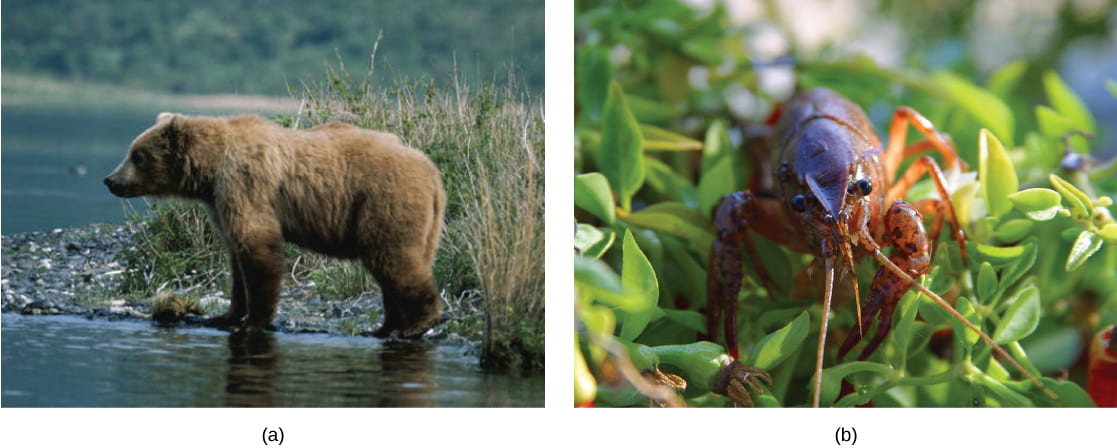
Omnivores are animals that consume both establish- and animal-derived food. In Latin, omnivore ways to swallow everything. Humans, bears and chickens are instance of vertebrate omnivores; invertebrate omnivores include cockroaches and crayfish.
Brute Nutritional Requirements (Human Focus)
Organic Precursors
The organic molecules required for edifice cellular material and tissues must come up from food. Carbohydrates or sugars are the primary source of organic carbons in the animal torso. During digestion, digestible carbohydrates are ultimately broken down into glucose and used to provide energy through metabolic pathways. Complex carbohydrates, including polysaccharides, can be cleaved down into glucose through biochemical modification; notwithstanding, humans do non produce the enzyme cellulase and lack the ability to derive glucose from the polysaccharide cellulose. In humans, these molecules provide the cobweb required for moving waste product through the large intestine and a healthy colon. The intestinal flora in the homo gut are able to extract some nutrition from these establish fibers. The backlog sugars in the trunk are converted into glycogen and stored in the liver and muscles for afterward utilise. Glycogen stores are used to fuel prolonged exertions, such as long-altitude running, and to provide free energy during food shortage. Backlog glycogen can be converted to fats, which are stored in the lower layer of the skin of mammals for insulation and energy storage. Excess digestible carbohydrates are stored past mammals in gild to survive famine and aid in mobility.
Another important requirement is that of nitrogen. Protein catabolism provides a source of organic nitrogen. Amino acids are the edifice blocks of proteins and poly peptide breakup provides amino acids that are used for cellular function. The carbon and nitrogen derived from these get the edifice cake for nucleotides, nucleic acids, proteins, cells, and tissues. Excess nitrogen must be excreted equally it is toxic. Fats add flavor to nutrient and promote a sense of satiety or fullness. Fatty foods are likewise pregnant sources of energy because one gram of fatty contains nine calories. Fats are required in the diet to aid the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins and the production of fat-soluble hormones.
Essential Nutrients
While the animal body can synthesize many of the molecules required for function from the organic precursors, in that location are some nutrients that need to be consumed from food. These nutrients are termed essential nutrients, meaning they must be eaten, and the body cannot produce them.
The omega-3 alpha-linolenic acid and the omega-6 linoleic acrid are essential fatty acids needed to brand some membrane phospholipids. Vitamins are another class of essential organic molecules that are required in small quantities for many enzymes to office and, for this reason, are considered to be co-enzymes. Absence or depression levels of vitamins can take a dramatic effect on health, as outlined in the tables below. Both fat-soluble and water-soluble vitamins must exist obtained from food. Minerals are inorganic essential nutrients that must be obtained from food. Amidst their many functions, minerals aid in structure and regulation and are considered co-factors. Certain amino acids also must be procured from food and cannot be synthesized by the torso. These amino acids are the “essential†amino acids. The human body tin can synthesize only 11 of the 20 required amino acids; the balance must be obtained from food in the form of protein. When eaten, proteins are broken down into their amino acid building blocks and are then used about immediately to synthesize new proteins needed past the torso. The essential amino acids are listed beneath (note, you are non required to memorize vitamins and minerals included in these tables).
| Water-soluble Essential Vitamins | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin | Function | Deficiencies Tin can Pb To | Sources |
| Vitamin Bane (Thiamine) | Needed by the body to process lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates Coenzyme removes CO2 from organic compounds | Muscle weakness, Beriberi: reduced heart function, CNS problems | Milk, meat, dried beans, whole grains |
| Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) | Takes an active function in metabolism, aiding in the conversion of food to energy (FAD and FMN) | Cracks or sores on the outer surface of the lips (cheliosis); inflammation and redness of the tongue; moist, scaly skin inflammation (seborrheic dermatitis) | Meat, eggs, enriched grains, vegetables |
| Vitamin B3 (Niacin) | Used by the body to release energy from carbohydrates and to process alcohol; required for the synthesis of sexual practice hormones; component of coenzyme NAD+ and NADP+ | Pellagra, which can result in dermatitis, diarrhea, dementia, and death | Meat, eggs, grains, basics, potatoes |
| Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic acid) | Assists in producing energy from foods (lipids, in particular); component of coenzyme A | Fatigue, poor coordination, retarded growth, numbness, tingling of hands and feet | Meat, whole grains, milk, fruits, vegetables |
| Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) | The principal vitamin for processing amino acids and lipids; also helps catechumen nutrients into energy | Irritability, depression, confusion, mouth sores or ulcers, anemia, muscular twitching | Meat, dairy products, whole grains, orangish juice |
| Vitamin Bseven (Biotin) | Used in energy and amino acid metabolism, fat synthesis, and fat breakup; helps the torso apply blood saccharide | Pilus loss, dermatitis, depression, numbness and tingling in the extremities; neuromuscular disorders | Meat, eggs, legumes and other vegetables |
| Vitamin B9 (Folic acid) | Assists the normal development of cells, especially during fetal development; helps metabolize nucleic and amino acids | Deficiency during pregnancy is associated with birth defects, such as neural tube defects and anemia | Leafy green vegetables, whole wheat, fruits, nuts, legumes |
| Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) | Maintains healthy nervous system and assists with blood cell germination; coenzyme in nucleic acid metabolism | Anemia, neurological disorders, numbness, loss of balance | Meat, eggs, beast products |
| Vitamin C (Ascorbic acrid) | Helps maintain connective tissue: bone, cartilage, and dentin; boosts the allowed system | Scurvy, which results in bleeding, hair and tooth loss; joint pain and swelling; delayed wound healing | Citrus fruits, broccoli, tomatoes, red sweet bong peppers |
| Fat-soluble Essential Vitamins | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin | Part | Deficiencies Can Atomic number 82 To | Sources |
| Vitamin A (Retinol) | Critical to the development of bones, teeth, and skin; helps maintain eyesight, enhances the immune system, fetal development, gene expression | Night-incomprehension, skin disorders, dumb immunity | Dark greenish leafy vegetables, yellow-orangish vegetables fruits, milk, butter |
| Vitamin D | Critical for calcium assimilation for bone evolution and strength; maintains a stable nervous organization; maintains a normal and strong heartbeat; helps in blood clotting | Rickets, osteomalacia, immunity | Cod liver oil, milk, egg yolk |
| Vitamin E (Tocopherol) | Lessens oxidative damage of cells, and prevents lung harm from pollutants; vital to the allowed arrangement | Deficiency is rare; anemia, nervous system degeneration | Wheat germ oil, unrefined vegetable oils, nuts, seeds, grains |
| Vitamin K (Phylloquinone) | Essential to blood clotting | Bleeding and like shooting fish in a barrel bruising | Leafy green vegetables, tea |
| Minerals and Their Function in the Human Trunk | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Mineral | Office | Deficiencies Tin Lead To | Sources |
| *Calcium | Needed for muscle and neuron part; heart health; builds bone and supports synthesis and function of blood cells; nervus function | Osteoporosis, rickets, muscle spasms, impaired growth | Milk, yogurt, fish, green leafy vegetables, legumes |
| *Chlorine | Needed for production of hydrochloric acid (HCl) in the stomach and nervus part; osmotic balance | Musculus cramps, mood disturbances, reduced appetite | Tabular array salt |
| Copper (trace amounts) | Required component of many redox enzymes, including cytochrome c oxidase; cofactor for hemoglobin synthesis | Copper deficiency is rare | Liver, oysters, cocoa, chocolate, sesame, nuts |
| Iodine | Required for the synthesis of thyroid hormones | Goiter | Seafood, iodized salt, dairy products |
| Iron | Required for many proteins and enzymes, notably hemoglobin, to prevent anemia | Anemia, which causes poor concentration, fatigue, and poor allowed function | Cherry meat, leafy light-green vegetables, fish (tuna, salmon), eggs, dried fruits, beans, whole grains |
| *Magnesium | Required co-gene for ATP formation; bone formation; normal membrane functions; musculus office | Mood disturbances, muscle spasms | Whole grains, leafy green vegetables |
| Manganese (trace amounts) | A cofactor in enzyme functions; trace amounts are required | Manganese deficiency is rare | Common in most foods |
| Molybdenum (trace amounts) | Acts as a cofactor for three essential enzymes in humans: sulfite oxidase, xanthine oxidase, and aldehyde oxidase | Molybdenum deficiency is rare | |
| *Phosphorus | A component of bones and teeth; helps regulate acid-base residuum; nucleotide synthesis | Weakness, bone abnormalities, calcium loss | Milk, hard cheese, whole grains, meats |
| *Potassium | Vital for muscles, eye, and nerve office | Cardiac rhythm disturbance, muscle weakness | Legumes, potato peel, tomatoes, bananas |
| Selenium (trace amounts) | A cofactor essential to action of antioxidant enzymes like glutathione peroxidase; trace amounts are required | Selenium deficiency is rare | Common in most foods |
| *Sodium | Systemic electrolyte required for many functions; acid-base of operations balance; water balance; nerve function | Muscle cramps, fatigue, reduced ambition | Tabular array common salt |
| Zinc (trace amounts) | Required for several enzymes such as carboxypeptidase, liver alcohol dehydrogenase, and carbonic anhydrase | Anemia, poor wound healing, can lead to short stature | Common in most foods |
| *Greater than 200mg/day required | |||
| Essential Amino Acids | |
|---|---|
| Amino acids that must be consumed | Amino acids anabolized by the body |
| isoleucine | alanine |
| leucine | selenocysteine |
| lysine | aspartate |
| methionine | cysteine |
| phenylalanine | glutamate |
| tryptophan | glycine |
| valine | proline |
| histidine* | serine |
| threonine | tyrosine |
| arginine* | asparagine |
| *The homo body can synthesize histidine and arginine, but not in the quantities required, particularly for growing children. | |
This video provides a summary of human nutrition needs:
What Animals Eat and Lives According to Their Structure
Source: https://organismalbio.biosci.gatech.edu/nutrition-transport-and-homeostasis/nutrition-needs-and-adaptations/






Comments
Post a Comment